* WHERE clause is used as a filter on the table to get a desired output. It is used to full fill a given condition.
Syntax:-
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE search_condition
ORDER BY expression;
- WHERE clause appears after the FROM clause but before the ORDER BY clause.
- WHERE clause not only is used in SELECT statement but also in the UPDATE and DELETE clause.
- We use ORDER BY clause at the very end of the query.
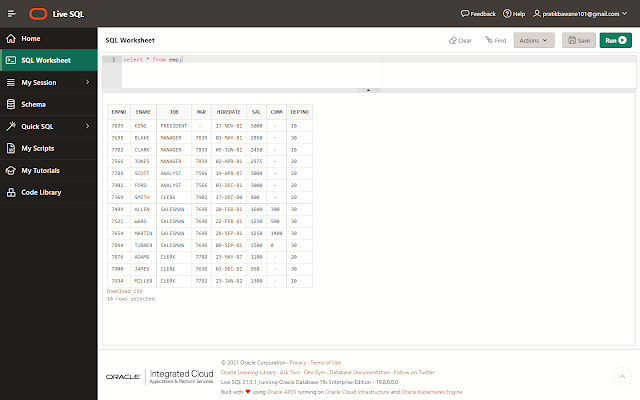
• Lets say we have the emp table:
and we want the names of the employees who's salary is greater than 2000.
• So we will write a query:
- As we can see, the data is now filtered out. Earlier there were 14 rows but now after using WHERE clause we have 6 rows.
- We always use WHERE clause with comparison operators like:
Now lets see ORDER BY clause:
• Say we have the same query viz "SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SAL>2000;" but now we want the data to be sorted in ascending order of sal column then we write--
SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SAL>2000 ORDER BY SAL;
• We can see the SAL column is now sorted in the ascending order. If we want to sort the data by descending order then just write desc viz a shorthand for descending.
SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SAL>2000 ORDER BY SAL DESC;
- We can also filter the data with the help of one or more columns
- We can even display one or more columns.






Comments
Post a Comment